ancientbruisesbrokenruses
74 posts
Latest Posts by ancientbruisesbrokenruses
My main problem as a writer is that I don’t write because “I have a story to tell”. I write because there are worlds I want to visit, ideas I want to explore, people I want to meet, conversations I want to hear, emotions that I want to express, and impossibilities I want to make real.
Which means that I still need a fucking plot.
ALSO! do you know how many fuckers have fucking cheated on their partners? A fuck load. You know this right? It’s not some great, mystical feat. He didn’t fuck a unicorn. Unlike Katherine the Great. I’m sorry that was a bad history joke. Or, I think it was funny. You’d get it if you weren’t an idiot. Are you an idiot? Oh right, you are. We covered this in my last one of these, didn’t we? I thought me did. Well, let me restate this. You’re an idiot. you’re welcome. Have a nice fucking day.
Slutshaming women is not ok Slutshaming Alexander Hamilton is totally ok Tumblr logic
Don’t know if anyone remembers this, but Alexander Hamilton was a real person. A pretty amazing person, if you ask me. And, that’s was one bloody time and then there was the whole mess with he Reynolds Pamphlet…He made a mistake, he owned up to it, didn’t try to make too many excuses(’it was an accident!’ ‘i swear, it just happened!’ ‘It all happened so fast!’ ‘i swear I didn’t mean it!’ ‘i love you!’ Etc). Do you want me to rant about John Laurens right now? I will, that way you won’t be able to use him against my argument. Which would be idiocy and I hope you aren’t an idiot.
Slutshaming women is not ok Slutshaming Alexander Hamilton is totally ok Tumblr logic
Not reply what they were asking, but Turn. Not only is it the Drarry fic, but it’s sort of like that. https://archiveofourown.org/works/879852/chapters/1692695 I love the narcissistic snake trope.
your blog really is a godsend! i’m looking for a fic where harry was under a curse (?) and basically it was an alternate universe where neville was the chosen one and he and draco were friends. it was basically harry’s entire life up to having kids and then he woke up from the curse and wasn’t with draco. i’m pretty sure they also went ice skating at some point after harry woke up from the curse. sorry it’s not much! thank you, have a great day :)
I’ve seen this similar theme before? My terrible memory is blank so I hope my lovely followers can help you :)
“like blowing bubbles”
That’s gay.

do magical kids get yearbooks??? this was such a great excuse to draw 16 portraits
I do not agree that’s it’s canon, it’s not. However. I do like the idea and am trying or incorporate it into my fic.
Black Hermione.
Reblog if you agree.
I’m curious...
reblog if what jkr says is no longer canon to you
obsessed with the idea of vampire snow white
How I Plan...
Building a story or series from the ground up with the help of templates!
This is how I approach planning. It covers what I do up to the point of opening a blank document and typing the first word.
Despite the tags this isn’t going to be ‘how to’ or advice based because who am I to tell you how to plan a story? This is only an option:) I engourage you to steal liberally but also question whether or not this method will work for you. If you don’t vibe with something, throw it out!

*you don’t have to answer these questions in order.
STRUCTURE LEVEL
Genre/Sub-genres: Picking a genre can help you find ideas/tropes faster. If you’ve written or read a book before you probably know the types of stories you like.
Age Category: This can help you find themes for you story. I like to sepate genre and cataegory since you can have a young adult or an adult romance.
Point Of View: Pick who will tell the story. Will there be more than one?
Tense: First, second or third person? Past or present?
Formatting: How will the story be split up? Through chapters or parts. I also like to put whether or not I’ll have a playlist, any quotes or epigraphs, prologues or epilogues, anything like that.
Tone: Will your story be serious, light hearted, sad, satirical...etc
Atmosphere/Color palette: I like to use this for when I’m writing description. Using specificities to elevate your writing can bring a world together and make it feel real.
Overall Concept: As vague as you’d like it to be! I usually give a few sentences.
Comparison Titles: I love to use comparison titles in the beginning when nothing has been solidified. It helps me know what came before me while still generating lots of inspiration.
SERIES LEVEL
Series Title: I usually base it off the first books title or a significant thing that links all the stories together.
Number of stories you want: I don’t always know how many stories will be in a series but it’s good to have a rough esimate of how many you’d like to write.
Number of stories realistically achievable: But we all know that sometimes an idea just isn’t sustainable for a 10 book series but works rather well as a trilogy instead.
Story that will kick off the series: All of your stories should fit a purpose in the series but this book will take the roll as a set-up (not to be confused as ‘filler’) for the rest of your series. It’s just something to have in mind when planning. This way you can plant twists and foreshadowing for the rest of the books.
Story that will close out the series: This story has big shoes to fill since you’ve probably been amping everything up to an explosive finish but at the end of the day it doesn’t matter if it’s bigger and better than what came before, it only matters if it’s a satisfying close to the whole series.
Summarize each story
Story # 1 summary ...you get the idea
Timeline: I like to know what year the series starts and when it will end. It might sound complicated but it’s so helpful. You don’t want a character to be pregnant or something for three books if the the stories have spanned more than nine months.
Spin-offs: You might find that you’ve got some ideas that don’t quite fit in with the others but they have some common elements. A spin-off is a cool way to explore those other ideas.
Naming conventions: I like to name my individual stories similar things to keep a theme. Example: J. R. Wards Black Dagger Brotherhood series has book titles with the word ‘Lover’ in them. There’s also naming conventions like the ACOTAR series by Sarah J. Maas that go “A Court of Blank and Blank”
SETTING LEVEL
Town/City/Village Name:
Area Description:
State/Province:
Country:
Common Weather:
Population:
Popular Figures:
Popular Locations:
Historical Background and Events:
What might the town be hiding to the average passer-by?
*You can definitely add more questions depending on your story. I write mostly within our world but I do like to create fictional towns.
CHARACTER LEVEL
Full Name:
Age:
Role:
Title/Rank/Occupation:
Wants:
Fears:
Misbelief:
Description/Faceclaim:
Personality Traits:
Zodiac Sign:
MBTI:
Theme Song:
Backstory:
Daily Life:
* Again, you can add any more questions you’d like to. These are just the ones I like to use to get going. Some of them are super vague, so in Daily Life I’ll put their living arrangement, transportation, pets or anything like that. I also add loads of stuff in their Description such as sexuality, how they dress, tattoos or scars, etc.
GROUP
*this is for anything like a fictional club, cult, company, evil organization or something like that.
Name:
Sub-divisions:
Type:
Founder:
History:
Current Leader:
Headquarters:
Current Operation:
Biggest Threat:
Biggest Allies:
Council Members (include roles):
Other Members (include roles):
STORY LEVEL
Working Title: Sometimes I use something concrete but if I need to get it out of the way I’ll put something like Project Black.
Estimated Length: Word or chapter count you’d like to achieve.
Order: Which book in the series is it?
Premise: I like to refer to this as the summary’s skeleton.
Tropes:
Subplot(s):
Story Summary:
Story Theme Song: This is just for fun but sometimes it really helps me capture what the whole story might be. I can also use it when I’m low on inspiration.
BEAT LEVEL
* I’d recommend googling an explanation of story beats or purchasing Blake Snyder or Jessica Brody’s book on Save The Cat beat sheet. But on the other hand, you don’t have to use a beat sheet at all. And if at any point during planning you feel like you’re ready to write then go for it!
Opening Image: An image that catapults your audience into the look and feel of your story
Theme Stated: Typically the theme of the story is communicated by someone fairly early on. This is dialogue spoken to the protagonist that he doesn’t quite grasp yet.
Set-Up: Show the protagonist in their “old world.” Let the audience know what the status quo is for them, then hint at the adventure that follows. This is also a time to introduce secondary characters.
Catalyst: Sometimes called the “inciting incident,” the catalyst is the event that disrupts your protagonist’s status quo. But they’re not ready to make the choice that catapults them into the story just yet.
Debate: This is where the protagonist has doubts about setting out on their perilous journey.
Break into Two: Inevitably, your protagonist will overcome their doubt and make a choice to set out on their adventure. This is the choice that sets the plot in motion. Your beat sheet will be filled with obstacles and twists resulting from making this choice from here on out.
B Story: A subplot ensues. Some would say that this is usually a romantic subplot.
Fun and Games: Plot structure requires a stretch where your protagonist wields their new power, and does cool stuff with it. I’ve also heard this referred to as the Promise of The Premise. So in Hunger Games by Susanne Collins this would be Katniss actually fighting in the games.
Midpoint: At some point, your protagonist will either get what they’re after... or not. But there will be consequences either way.
Bad Guys Close In: After your protagonist gets what they want, or not, there will be consequences. These forces will tighten their grasp, and throw the protagonist off balance.
All Is Lost: The dire circumstances your protagonist endures will lead to an inevitable loss. Which can be anything but it most commonly a character death.
Dark Night of the Soul: At this point of the Save the Cat beat sheet template, your protagonist has lost hope.
Break into Three: In plot structure, this is where your protagonist claws around in the darkness, only to find or remember something useful.
Finale: Treat the finale as the Act 3 summary. The Save the Cat beat sheet template is at its end, so it’s time for the protagonist to take on their foes. Armed with new tools and self-discoveries, the protagonist often synthesizes what they've learned (in Act 2) with values they've always had (Act 1).
Final Image: Along with the opening image, the final image creates the bookend that encapsulates the journey. This is the last thing the audience is left with.
*Closing thoughts: I have never used just a beat sheet because they don’t resonate with me for every story. I always add stuff or take away. I think there is a special beat missing between the Finale and Final image and that is where the characters slow down, take a breath and reflect on everything they’ve experienced. I also think Romance is the hardest genre to use the beat sheet with but I do a hybrid of the Beat Sheet from Save The Cat Writes A Novel! By Jessica Brody and Romancing the Beat by Gwen Hayes for the most part.
NOW JUST WRITE! :)
I hope this was helpful in some way or another! DM me or reply with any questions or for clarification. I have many more posts I’d like to create (on my process) but if you have any ideas or topics I should make posts on let me know.
Good luck and happy writing!
How I Plan...
Building a story or series from the ground up with the help of templates!
This is how I approach planning. It covers what I do up to the point of opening a blank document and typing the first word.
Despite the tags this isn’t going to be ‘how to’ or advice based because who am I to tell you how to plan a story? This is only an option:) I engourage you to steal liberally but also question whether or not this method will work for you. If you don’t vibe with something, throw it out!

*you don’t have to answer these questions in order.
STRUCTURE LEVEL
Genre/Sub-genres: Picking a genre can help you find ideas/tropes faster. If you’ve written or read a book before you probably know the types of stories you like.
Age Category: This can help you find themes for you story. I like to sepate genre and cataegory since you can have a young adult or an adult romance.
Point Of View: Pick who will tell the story. Will there be more than one?
Tense: First, second or third person? Past or present?
Formatting: How will the story be split up? Through chapters or parts. I also like to put whether or not I’ll have a playlist, any quotes or epigraphs, prologues or epilogues, anything like that.
Tone: Will your story be serious, light hearted, sad, satirical...etc
Atmosphere/Color palette: I like to use this for when I’m writing description. Using specificities to elevate your writing can bring a world together and make it feel real.
Overall Concept: As vague as you’d like it to be! I usually give a few sentences.
Comparison Titles: I love to use comparison titles in the beginning when nothing has been solidified. It helps me know what came before me while still generating lots of inspiration.
SERIES LEVEL
Series Title: I usually base it off the first books title or a significant thing that links all the stories together.
Number of stories you want: I don’t always know how many stories will be in a series but it’s good to have a rough esimate of how many you’d like to write.
Number of stories realistically achievable: But we all know that sometimes an idea just isn’t sustainable for a 10 book series but works rather well as a trilogy instead.
Story that will kick off the series: All of your stories should fit a purpose in the series but this book will take the roll as a set-up (not to be confused as ‘filler’) for the rest of your series. It’s just something to have in mind when planning. This way you can plant twists and foreshadowing for the rest of the books.
Story that will close out the series: This story has big shoes to fill since you’ve probably been amping everything up to an explosive finish but at the end of the day it doesn’t matter if it’s bigger and better than what came before, it only matters if it’s a satisfying close to the whole series.
Summarize each story
Story # 1 summary ...you get the idea
Timeline: I like to know what year the series starts and when it will end. It might sound complicated but it’s so helpful. You don’t want a character to be pregnant or something for three books if the the stories have spanned more than nine months.
Spin-offs: You might find that you’ve got some ideas that don’t quite fit in with the others but they have some common elements. A spin-off is a cool way to explore those other ideas.
Naming conventions: I like to name my individual stories similar things to keep a theme. Example: J. R. Wards Black Dagger Brotherhood series has book titles with the word ‘Lover’ in them. There’s also naming conventions like the ACOTAR series by Sarah J. Maas that go “A Court of Blank and Blank”
SETTING LEVEL
Town/City/Village Name:
Area Description:
State/Province:
Country:
Common Weather:
Population:
Popular Figures:
Popular Locations:
Historical Background and Events:
What might the town be hiding to the average passer-by?
*You can definitely add more questions depending on your story. I write mostly within our world but I do like to create fictional towns.
CHARACTER LEVEL
Full Name:
Age:
Role:
Title/Rank/Occupation:
Wants:
Fears:
Misbelief:
Description/Faceclaim:
Personality Traits:
Zodiac Sign:
MBTI:
Theme Song:
Backstory:
Daily Life:
* Again, you can add any more questions you’d like to. These are just the ones I like to use to get going. Some of them are super vague, so in Daily Life I’ll put their living arrangement, transportation, pets or anything like that. I also add loads of stuff in their Description such as sexuality, how they dress, tattoos or scars, etc.
GROUP
*this is for anything like a fictional club, cult, company, evil organization or something like that.
Name:
Sub-divisions:
Type:
Founder:
History:
Current Leader:
Headquarters:
Current Operation:
Biggest Threat:
Biggest Allies:
Council Members (include roles):
Other Members (include roles):
STORY LEVEL
Working Title: Sometimes I use something concrete but if I need to get it out of the way I’ll put something like Project Black.
Estimated Length: Word or chapter count you’d like to achieve.
Order: Which book in the series is it?
Premise: I like to refer to this as the summary’s skeleton.
Tropes:
Subplot(s):
Story Summary:
Story Theme Song: This is just for fun but sometimes it really helps me capture what the whole story might be. I can also use it when I’m low on inspiration.
BEAT LEVEL
* I’d recommend googling an explanation of story beats or purchasing Blake Snyder or Jessica Brody’s book on Save The Cat beat sheet. But on the other hand, you don’t have to use a beat sheet at all. And if at any point during planning you feel like you’re ready to write then go for it!
Opening Image: An image that catapults your audience into the look and feel of your story
Theme Stated: Typically the theme of the story is communicated by someone fairly early on. This is dialogue spoken to the protagonist that he doesn’t quite grasp yet.
Set-Up: Show the protagonist in their “old world.” Let the audience know what the status quo is for them, then hint at the adventure that follows. This is also a time to introduce secondary characters.
Catalyst: Sometimes called the “inciting incident,” the catalyst is the event that disrupts your protagonist’s status quo. But they’re not ready to make the choice that catapults them into the story just yet.
Debate: This is where the protagonist has doubts about setting out on their perilous journey.
Break into Two: Inevitably, your protagonist will overcome their doubt and make a choice to set out on their adventure. This is the choice that sets the plot in motion. Your beat sheet will be filled with obstacles and twists resulting from making this choice from here on out.
B Story: A subplot ensues. Some would say that this is usually a romantic subplot.
Fun and Games: Plot structure requires a stretch where your protagonist wields their new power, and does cool stuff with it. I’ve also heard this referred to as the Promise of The Premise. So in Hunger Games by Susanne Collins this would be Katniss actually fighting in the games.
Midpoint: At some point, your protagonist will either get what they’re after... or not. But there will be consequences either way.
Bad Guys Close In: After your protagonist gets what they want, or not, there will be consequences. These forces will tighten their grasp, and throw the protagonist off balance.
All Is Lost: The dire circumstances your protagonist endures will lead to an inevitable loss. Which can be anything but it most commonly a character death.
Dark Night of the Soul: At this point of the Save the Cat beat sheet template, your protagonist has lost hope.
Break into Three: In plot structure, this is where your protagonist claws around in the darkness, only to find or remember something useful.
Finale: Treat the finale as the Act 3 summary. The Save the Cat beat sheet template is at its end, so it’s time for the protagonist to take on their foes. Armed with new tools and self-discoveries, the protagonist often synthesizes what they've learned (in Act 2) with values they've always had (Act 1).
Final Image: Along with the opening image, the final image creates the bookend that encapsulates the journey. This is the last thing the audience is left with.
*Closing thoughts: I have never used just a beat sheet because they don’t resonate with me for every story. I always add stuff or take away. I think there is a special beat missing between the Finale and Final image and that is where the characters slow down, take a breath and reflect on everything they’ve experienced. I also think Romance is the hardest genre to use the beat sheet with but I do a hybrid of the Beat Sheet from Save The Cat Writes A Novel! By Jessica Brody and Romancing the Beat by Gwen Hayes for the most part.
NOW JUST WRITE! :)
I hope this was helpful in some way or another! DM me or reply with any questions or for clarification. I have many more posts I’d like to create (on my process) but if you have any ideas or topics I should make posts on let me know.
Good luck and happy writing!
How to write about Grief:
There is no right or wrong way to experience grief. Just as there is no right or wrong way to write it. Everyone is different, each set of circumstances are different.
The point of this post is to show you how different people react in different ways, and give points on how you might write that, depending on your character and story.
Reactions to Grief
Numbness: Your character may go into auto-pilot and be unable to process the events that have unfolded.
Anger: This can be aimed at other people, at a Higher Being, or at nothing in particular.
Unsteady: Your characters may be unsteady. For example, unable to stop their voice from shaking or they may find it difficult to stand.
Focusing on Others: Your character may disregard their own feelings because they are so overwhelmed and instead concentrate on someone else’s well-being.
Seek out routines: Amid upheavals, your character may seek comfort in tasks that are familiar and “safe,” such as working, cleaning, making their bed, making absurd amounts of tea or taking a morning walk.
Pretending that Everything Is Okay: Grief is viewed as an emotion that should cease or be concealed once the funeral is over. So people mention the news in an offhand comment, then talk and laugh as if all is right with the world.
Denial: Some people deny the reality of death and convince themselves that the news is a joke or can’t be true.
Reactions from people surrounding your character:
People may avoid your character as they do not know what to say or simply can’t find the right words.
Some may even go as far as to cross the street when they notice your character approaching.
Even people that the character has known for years may act strange or standoff-ish, simply because they don’t know what to say.
On the other side of that, some people may be overly helpful and friendly.
It is not uncommon for estranged friends, family or others to suddenly reappear in a person’s life after they have experienced grief.
Either because those people want to offer their support and love or because they’re being nosy and they want to be kept up to date on the “drama”.
Most people will move on from the event fairly quickly if they weren’t emotionally invested.
Some people may even get annoyed at your character for still being upset weeks or months later.
When talking about the person they have lost:
Your character may recall a memory or tell a story about their loved one, these are possible reactions. (I have encountered all of them.)
Your character may being to cry or get upset at the thought of the person they have lost.
The person they are talking to may become awkward and avert eye contact when your character brings up the person they have lost.
Others may ask or tell your character to stop talking about the person they have lost. They may roll their eyes, cough awkwardly, or cut off your character mid sentences so that they can change the subject.
Some people may ask inappropriate questions about the circumstances in which the character’s loved one passed away. Depending on the personality of your character then may react differently.
Other things to note:
Grief is not constrained by time.
One of the main problems with grief in fiction is that a character is typically heartbroken for a couple scenes and then happy again. But grief does not evaporate because the world needs saving.
Allow your character to wrestle with their grief.
Your character may feel guilty. Your character may feel a twinge of guilt when they laugh or have a good time with someone else; when they do something to remind them that they’re alive, and their loved one isn’t.
Grief is a game changer. A previously outgoing character may withdraw and isolate themselves. Some people may take grief and/or bereavement as a sign that life is too short; they may make big decisions in an attempt to make themselves feel better and grow away from their pain.
Sometimes grief can help you find your purpose.
At first grief can be all consuming. It hurts and you can’t really control it. It may seem unrelenting. Eventually the grief will become easier to deal with, your character may find the days to be better, but that doesn’t mean that when the grief hits it doesn’t hurt any less.
For most people, grief never really goes away. “Sometimes you have to accept the fact that certain things will never go back to how they used to be.”
It is rare that a person will ever give a long speech about their feelings, a lot of people struggle to even find the words. But that’s okay. Show the reader how your character feels, rather than just telling them.
Don’t pause the plot to deal with the aspect of grief. This could overwhelm the readers and drag the pace down. In reality, life doesn’t just stop due to grief, the world keeps spinning and things still need to be done. Use the character’s grief as a backdrop for the story’s events.
Yes, grief affects the character’s day-to-day life, goals, and relationships. But it shouldn’t drive readers away or stagnate the story. Instead, should engage readers and produce empathy that keeps them turning pages.
You don’t need to tell your readers that everything will be fine. You don’t need to provide all of the answers.
“Skirting grief and treating it lightly is easy. But by realistically portraying it through a variety of responses and its lasting effects on the character’s life, readers will form a connection with your characters.“
Beautiful words but WHAT IS THAT PEN? I WANT THAT PEN!

Did some writing today :) these are not my words ! The author is unknown (yes, i researched and came up with nothing) so I’m not trying to take away from their work!
I need to start journaling again 🌙🌞
That must be the one I’m thinking of, thank you.

I feel like I should just add on to this with a not-really-related fact that someone is going to have to clarify. I read a long time ago(during a time when I had the want to actually do stuff instead of just sleep, blow off online school, almost ignore my homework, eat ice cream and watch tele while saying “fuck you” to the world) that, somewhere not in the states, they stopped treating addiction like a crime and more like something that needed to be helped, like a mental disorder or something. If you had a certain amount, then you would meet with two people, I don’t remember what they were. A social worker and a lawyer, maybe. This is why I need someone to fill in the ever present blanks. The drug rate or whatever dropped astoundingly.

I’m white. I know that. I don’t pretend I’m not. But gods do I hate that teacher right now. She’s not saying that at she doesn’t like the fact that you like fucking pineapples on your pizza, she’s saying that your ‘opinion’ literally goes against her entire fucking existence.
GO 👏 THE 👏 FUCK 👏 OFF. Also, the American educational system is trash. I applaud this child’s parents for giving her a voice and standing up against bias authority.
So You Want Your OC to be Jewish
So you’re writing a story and you want to make a Jewish character—great! I’m here to help. I always want more Jewish representation but I want good Jewish representation, so this is my attempt to make a guide to making a Jewish character. What are my credentials? I’m Jewish and have been my whole life. Obligatory disclaimer that this is by no means comprehensive, I don’t know everything, all Jews are different, and this is based on my experiences as an American Jew so I have no idea, what, if any, of this applies to non-American Jews.
If there’s anything you want me to make a post going more into detail about or if there’s anything I didn’t mention but you want to know please ask me! I hope this is helpful :) Warning, this is long.
Keep reading
DON’T FORGET THIS APPLIES TO PEOPLE!!!!


❤ Give love! Spread love! ❤
Go and tell your favorite artist something nice about their art! Go-go-go!
This has made me think so much…and not entirely about my characters.
Writing Grief
I’ve heard from many places - and wholeheartedly stand by - the idea that the larger the scope you’re trying to portray, the smaller your focus should be. For example, if you’re writing about a village that’s been destroyed, you don’t focus on the destruction everywhere, you focus on a little child’s doll lying half-scorched in the street. The idea is to channel as much of the emotion as possible into the smallest details. That’s how it’s the most potent.
Grief is one of these big things. Grief rocks your world, and it’s grip doesn’t go away as soon as the next thing comes around. It strikes at odd moments.
The thing with grief is that everyone experiences it differently, and everyone’s got different memories surrounding it. Given this fact, I’m going to describe questions who’s answers you may incorporate into your narrative, but I cannot give you a “this is how to write your character’s grieving.” The questions I’ve listed below are likely going to be most relevant at or just after another character’s died, when things are freshest and at their most raw.
(note: “or” questions do not necessarily mean you have to choose one or the other. You can, but it’s also saying, “is at least one of these the case?”)
How does it feel externally?
Do things feel too rough, or too soft? Too squishy or too unyielding?
Are yoru character’s sleeves damp or wet from wiping away tears? are there balls of tissues held tight in your character’s fists?
Is the air too cold or too warm?
Is the space too tight, or too open?
How does it feel physically internally?
Is your character’s jaw clenched or their muscles tightened?
Do their eyes sting or feel puffy from tears?
Are they dehydrated and/or hungry?
Does their skin feel cold to the touch?
Do they crave physical contact such as hugs, or do they not want to be touched?
How does your character feel emotionally?
Are they angry, scared, sad, or unsure?
Do they feel emotionally empty like there is nothing inside of them (do they feel cold but aren’t physically cold)?
Are their thoughts coherant, or are they scattered?
What do they notice? Colors, shapes, patterns, sounds, movement, tactile sensations, smells?
Is your character craving a sense or normalcy, or a sense of difference that reflects the difference of someone dying?
How does your character physically react?
Do they start crying or showing other intense emotions?
Do they try to hold everything inside and/or not show other people?
Does their movement style change (they’re jerkier, slower, etc)?
Do they not seem to hear anything anyone else is saying?
Do they try to overcompensate and/or pretend that what happened didn’t really matter (showing intense emotions seemingly unrelated to grief)?
#storychronology
"Start in the middle”
Story chronology: a few options
You might have heard about the advice “in medias res”: to begin your story at a point when the action has already begun.
I will illustrate this point with an example. It’s a simple story I made up for this post, but you get the picture. [Extensive image descriptions below the cut.]

In medias res (Latin for ‘in the middle of things’), will tell you that you shouldn’t begin this story with scene A, because there is little action in it. Scene B is also not particularly exciting, and both A and B are not very representative of the story that is to come. The most exciting scenes in this list are F and G.
There are a few versions of how you can start your story.
1. You could start your story with scene C, and tell your story chronologically from there, so you skip A and B:

2. You could start your story with scene F, and then go back to the beginning:

3. Or you can do the same with scene G first: how did she get into this mess?

4. You could start your story with scene F or G, and go back, but ditch A and B because they don’t fit in the theme of the story.

or

5. You could start with scene G or F and throw away the entire chronology. Maybe scene B is a flashback when she sits at the police station and waits to make her phonecall. She can imagine the conversation with her parents and wishes she was back in the orchard she used to play at when she was 8.

Personally, I don’t like option 2 and 3, because the less exciting scenes A and B feel even more boring after an exciting scene like F and G. But I’m just pointing out the options.
When you set out to outline a story, make it linear at first, make sure every causal relationship is sound, and then play around with the order of the scenes to make it more interesting.
I hope this was helpful. Don’t hesitate to ask me any questions, and happy writing!
Follow me for more writing advice, or check out my other writing advice here. New topics to write advice about are also always welcome.
Tag list below, a few people I like and admire and of course, you can be too. If you like to be added to or removed from the list, let me know.
Extensive image descriptions also below the cut.
Keep reading
#writinganactionscenewhenyousuckatwritingaction
Advice for people who are better at writing dialogue than action
As someone who has always been able to spit out witty quotes but couldn’t write a fight scene to save my life, here are some tips that have helped me that I would like to share.

1.) Go bit by bit.
Let’s get the hard one out of the way first. I’m going to use ‘fight scene’ for this example, but it can apply to just about any action scene. Have a starting point and an ending point, then just start writing. So let’s say two characters threaten each other. Okay. One takes a swing. Alright. What next? Maybe another one swings back. What next? First one kicks. Is it appropriate for character 1 to stab character 2 yet? Probably not. What can I do instead? Just work it out one action at a time. If it doesn’t come out the best on paper, who cares? You have a baseline. This isn’t easy and maybe not the best way to do it, but it’s a method I’ve used and it’s better than just saying “They fought until character 2 was stabbed.”

2.) Mix in Dialogue
Just use what you’re good at, fam’. Direct the action with dialogue. If you’re like me and your characters have an affinity for arguing with each other, sometimes their conversation will give you a better idea of what’s going on anyway. I mean, I essentially have a chase scene where one character gets shot and the conversation goes as follows.
*H shoots D*
C: Ooh, bad shot.
J: that’s what you have to say to that?
That’s not a great example, but this is also from a scene I’ve rewritten like ten times.
I mean, also, what about the “turn around slowly” scenes in horror movies?
I also use this sometimes to informally describe how a rock looks like the middle finger or something because the characters think it’s funny. It helps me, at the very least.
Point being, use your characters’ thoughts to give the reader a deeper idea of what’s going on if it’s hard for you to explain it outright.

3.) Write Dialogue First
First go in and write whatever the characters are discussing before going in and filling in the action. Do what you like and feel comfortable doing first, then perfect it later on. If it’s a fight scene, maybe the characters are sharing insults. Write the insults and then conduct the action to fit the rising tension accompanying the verbal insults. Don’t get writers block over the action; save it for when you have the energy.

4.) Just Keep It Simple
As a perfectionist with anxiety, I try to make my first drafts perfect. Spoiler alert: YOUR FIRST DRAFT WILL NEVER BE PERFECT. Life is too short to get upset over your weak action scenes. Write simple sentences and get the basis down. Who cares? Certainly not me at this point. When you go back and edit, then you can flip them around, add color and flavor, and make them come to life. But in the first draft? It’s perfectly okay if your action scene is “He ran towards her. He hugged her. She hugged him. They went home.” Later, you can go in and add things like “They embraced each other, tears in their eyes, never expecting to let go.” It’s okay if you’re not there. One step at a time, fam’.

If anyone else has any suggestions or tips for people who struggle with dialogue, feel free to add! These are just what has helped me through the years.
#actionwritingreferenceone
How do you write a fight scene without becoming repetitive? I feel like it just sounds like "she did this then this then this." Thanks so much!
I watch her as she fights. Her left leg flies through the air – a roundhouse – rolling into a spin. She misses, but I guess she’s supposed to. Her foot lands and launches her into a jump. Up she goes again, just as fast. The other leg pumps, high knee gaining altitude. The jumping leg tucks. Her body rolls midair, momentum carrying her sideways. She kicks. A tornado kick, they call it. The top of her foot slams into Rodrigo’s head, burying in his temple. Didn’t move back far enough, I guess.
His head, it snaps sideways like a ball knocked off a tee. Skull off the spine. His eyes roll back, and he slumps. Whole body limp. Legs just give out beneath him. He clatters to the sidewalk; wrist rolling off the curb.
She lands, making the full turn and spins back around. Her eyes are on his body. One foot on his chest. I don’t know if he’s alive. I don’t know if she cares. Nah, she’s looking over her shoulder. Looking at me.
The truth twists my gut. I should’ve started running a long time ago.
The first key to writing a good fight scene is to tell a story. The second key is having a grasp of combat rules and technique. The third is to describe what happens when someone gets hit. The fourth is to remember physics. Then, roll it all together. And remember: be entertaining.
If you find yourself in the “and then” trap, it’s because you don’t have a firm grasp of what exactly it is your writing. “He punched” then “She blocked” then “a kick” only gets you so far.
You’ve got to get a sense for shape and feeling, and a sense of motion. Take a page from the comic artist’s playbook and make a static image feel like it’s moving. Try to remember that violence is active. Unless your character is working with a very specific sort of soft style, they’re attacks are going to come with force. So, you’ve got to make your sentences feel like your hitting something or someone.
“Ahhh!” Mary yelled, and slammed her fist into the pine’s trunk. A sickening crack followed, then a whimper not long after.
Angie winced. “Feel better?”
Shaking out her hand, Mary bit her lip. Blood dripped from her knuckles, uninjured fingers gripping her wrist. She sniffed, loudly. “I…” she paused, “…no.”
“You break your hand?”
“I think so. Yeah.”
“Good,” Angie said. “Think twice next time before challenging a tree.”
Let your characters own their mistakes. If they hit something stupid in anger, like a wall or a tree then let them have consequences.Injury is part of combat. In the same way, “I should be running now” is. When the small consequences of physical activity invade the page, they bring reality with them.
People don’t just slug back and forth unless they don’t know how to fight, or their only exposure to combat is mostly movies or bloodsport like boxing. Either way, when one character hits another there are consequences. It doesn’t matter if they blocked it or even deflected it, some part of the force is going to be transitioned into them and some rebounds back at the person who attacked.
Your character is going to get hurt, and it’ll be painful. Whether that’s just a couple of bruises, a broken bone, or their life depends on how the fight goes.
However, this is fantasy. It is all happening inside our heads. Our characters are never in danger unless we say they are. They’ll never be hurt unless we allow it. A thousand ghost punches can be thrown and mean absolutely, utterly nothing at all to the state of the character. This is why it is all important to internalize the risks involved.
The writer is in charge of bringing a dose of reality into their fictional world. It is much easier to sell an idea which on some level mimics human behavior and human reactions. The ghost feels physical because we’ve seen it happen on television or relate to it happening to us when we get injured.
You’ve got five senses, use them. You know what it feels like to get injured. To be bruised. To fall down. To be out of breath. Use that.
Here’s something to take with you: when we fight, every technique brings us closer together. Unless it specifically knocks someone back. You need specific distances to be able to use certain techniques. There’s the kicking zone, the punching zone, and the grappling zone. It’s the order of operation, the inevitable fight progression. Eventually, two combatants will transition through all three zones and end up on the ground.
So, keep the zones in mind. If you go, “she punched, and then threw a roundhouse kick” that’s wrong unless you explain more. Why? Because if the character is close enough to throw a punch, then they’re too close to throw most kicks. The roundhouse will just slap a knee or a thigh against the other character’s ribs, and probably get caught. If you go, “she punched, rammed an uppercut into his stomach, and seized him by the back of the head”, then that’s right. You feel the fighters getting progressively closer together, which is how its supposed to work.
Use action verbs, and change them up. Rolled, rotated, spun, punched, kicked, slammed, rammed, jammed, whipped, cracked, etc.
You’ve got to sell it. You need to remember a human’s bodily limits, and place artificial ones. You need to keep track of injuries, every injury comes with a cost. Make sure they aren’t just trading blows forever.
I’ve seen advice that says fights all by themselves aren’t interesting. I challenge that assertion. If you’re good at writing action, then the sequence itself is compelling. You know when you are because it feels real. Your reader will tune out if it isn’t connecting, and the fight scene is a make or break for selling your fantasy. It is difficult to write or create engaging, well choreographed violence that a reader can easily follow and imagine happening.
-Michi
This blog is supported through Patreon. If you enjoy our content, please consider becoming a Patron. Every contribution helps keep us online, and writing. If you already are a Patron, thank you.
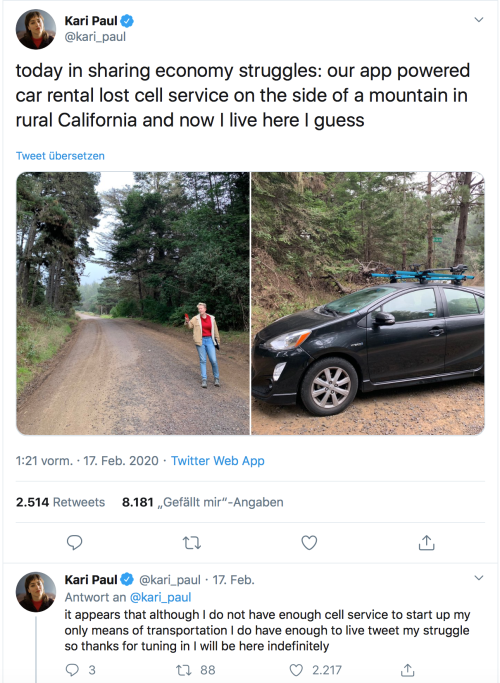
Welcome to the future, where you don’t own anything and the stuff you rent stops working once your phone has no signal.
YOU KNOW WHAT BOTHERS ME
when fantasy books describe the cloth of Quant Farmpeople’s clothing as “homespun” or “rough homespun”
“homespun” as opposed to what??? EVERYTHING WAS SPUN AT HOME
they didn’t have fucking spinning factories, your pseudo-medieval farmwife is lucky if she has a fucking spinning wheel, otherwise she’s spinning every single thread her family wears on a drop spindle NO ONE ELSE WAS DOING THE SPINNING unless you go out of your way to establish a certain baseline of industrialization in your fake medieval fantasy land.
and “rough”??? lol just because it’s farm clothes? bitch cloth was valuable as fuck because of the labor involved ain’t no self-respecting woman gonna waste fiber and ALL THAT FUCKING TIME spinning shitty yarn to weave into shitty cloth she’s gonna make GOOD QUALITY SHIT for her family, and considering that women were doing fiber prep/spinning/weaving for like 80% of their waking time up until very recently in world history, literally every woman has the skills necessary to produce some TERRIFYINGLY GOOD QUALITY THREADS
come to think of it i’ve never read a fantasy novel that talks about textile production at all??? like it’s even worse than the “where are all the farms” problem like where are people getting the cloth if no one’s doing the spinning and weaving??? kmart???


colored some doodles
🕯 🕯 this is a summoning spell to get dancing queen by abba into the umbrella academy season three 🕯 🕯
Likes charge reblog cast
Fantasy Guide to Make-Up and Cosmetics

If I am to be completely honest with you all, I know nothing about make-up. Those little brushes and endless sponges mean nothing to me except the fact that they are really soft and sometimes shiny. I don't wear makeup so you can imagine how useless I am at modern make-up.
However, history is my jam and I know about what make-up they use centuries ago. So never fear @theflyingravenbird I got you.
Ingredients and Applications


Make-up and cosmetics of the past were usually sourced from natural ingredients. The more difficult the ingredients were the more expensive the cosmetic was. Natural dies such as red ochre and berries were used to stain lips or colour powder to use as blusher to add colour to the lips. For examples:
Geishas of Japan are probably the most recognizable make-up wearers in the world. Historically and in some more traditional okiyas, the geishas painted their faces with rice powder to give them that unbroken, white complexion. A popular recipe for their crimson lipsticks involved extracting pigment from crushed safflower petals.
Henna paste made from the eponymous plant can be used as hair dye and to trace designs on the feet and hands.
Kohl is a black powder that is famous for its popularity in Egyptian Cultures and even the Persian Empire. Kohl lines the eyes like modern eyeliners and is found when one grounds stibnite. Kohl actually had the luck of preventing eye infections which no doubt helped in the climate of Egypt and beyond.
The Phoenicians used powdered metals of gold, silver and other metals to dust their faces. This is reputably thought to denote their wealthy status.
Rouge or blusher has had numerous recipes throughout history. The Ancient Egyptians made rouge from red ochre and animal fat. The Romans made their rouge from lead and cinnabar, which sounds about as bad for you as you think it does. The Ancient Greeks made it from pressed mulberries or other fruits such as beet and strawberries. The Ancient Chinese made rouge from extracts of coloured flowers.
Ancient Chinese cultures used a mixture of gumarabic, gelatin, beeswax, and eggs to stain their nails. The colors were often used to denote social class. Gold and silver was worn by royalty or black and red. The lower classes were not prohibited to wear bright colours.
Lipstick has also a few recipes. Egyptians used pounded carmine, a kind of insect, to smear on their lips. Other ancient civilizations used red ochre. Vermilion (though toxic) was also used, along with crushed flowers with red pigment mixed with beeswax during the Elizabethan period.
During the late Elizabeth and then again in the Baroque period, women and some men began to paint their faces with white powder. The layer of white lead and vinegar, or ceruse was popular for tears despite the hair loss and death it caused.
Make Up Tools

Powderpuffs: the powderpuff was a pad of soft material meant to apply powder to one's face. They were made of feathers, cotton or sheep's fleece.
Brushes: Brushes have been been around for ever. They have been found in some of the earliest Egyptian tombs. The brushes were often made from animal hair with wooden or more expensive handles.
Pots of pigment, scents and ointments: Some early tombs excavated from ancient civilizations have included what amounts to a palette (thank you lil sis for that word). The pigments in the pots would be very expensive. Ointments and balms have also been found. Perfumes were very popular in antiquity and made a recurrence in Europe after the Crusades (which helped since some of the make up smelled awful).
Make Up and Social standing


Though make up is rather popular now, it had a rather uncertain rise to popularity.
Most Ancient civilizations wore some kind of cosmetic. The overuse of cosmetics in ancient times was frowned on as prostitutes and actors often wore dramatic make up however the elite often smeared themselves with powders to make them paler and redden their cheeks.
In the Middle Ages, makeup had a dual reputation. The Church frowned on it because it was again popular with prostitutes and actors but it was a common consensus that if the woman was scarred from smallpox or some other disease she was excused from being labelled as vain.
In the late Elizabethan period, theatres were getting more popular and as was makeup. Actors began wearing make up more frequently as did the elite. Elizabeth I herself was infamous for her milk-white skin. Make up became more sociably acceptable among the rich and noble at this point.
The 1700s probably saw the height of make up madness. Both women and men of the elite powdered themselves with white lead paint. They rouged their cheeks to high pigment and stuck small dots of felt to cover blemishes. The commons began to poke fun at the elite's strange obsession with looking like they've lost all their blood. Dandies and painted noblewomen were often poked fun at by pamphlets and satirical cartoons.
The Victorians frowned on make up, thinking it garish and common. Queen Victoria herself denounced make up as uncouth which lead the elite to abandon it in droves. However, most women prized a clear complexion so there was a lot of secret make-up-ing going on.
During the Edwardian period and the 1920s, make up began to get more popular. Older more respectable women began trying makeup to fresh their complexion. The younger generations began to experiment with makeup leading to the infamous smokey eye look.
Jez believes in justice
Aureli believes in mercy
Scipio believes in what the situation calls for
does your oc believe in justice, or mercy?
Fantasy Guide to Make-Up and Cosmetics

If I am to be completely honest with you all, I know nothing about make-up. Those little brushes and endless sponges mean nothing to me except the fact that they are really soft and sometimes shiny. I don't wear makeup so you can imagine how useless I am at modern make-up.
However, history is my jam and I know about what make-up they use centuries ago. So never fear @theflyingravenbird I got you.
Ingredients and Applications


Make-up and cosmetics of the past were usually sourced from natural ingredients. The more difficult the ingredients were the more expensive the cosmetic was. Natural dies such as red ochre and berries were used to stain lips or colour powder to use as blusher to add colour to the lips. For examples:
Geishas of Japan are probably the most recognizable make-up wearers in the world. Historically and in some more traditional okiyas, the geishas painted their faces with rice powder to give them that unbroken, white complexion. A popular recipe for their crimson lipsticks involved extracting pigment from crushed safflower petals.
Henna paste made from the eponymous plant can be used as hair dye and to trace designs on the feet and hands.
Kohl is a black powder that is famous for its popularity in Egyptian Cultures and even the Persian Empire. Kohl lines the eyes like modern eyeliners and is found when one grounds stibnite. Kohl actually had the luck of preventing eye infections which no doubt helped in the climate of Egypt and beyond.
The Phoenicians used powdered metals of gold, silver and other metals to dust their faces. This is reputably thought to denote their wealthy status.
Rouge or blusher has had numerous recipes throughout history. The Ancient Egyptians made rouge from red ochre and animal fat. The Romans made their rouge from lead and cinnabar, which sounds about as bad for you as you think it does. The Ancient Greeks made it from pressed mulberries or other fruits such as beet and strawberries. The Ancient Chinese made rouge from extracts of coloured flowers.
Ancient Chinese cultures used a mixture of gumarabic, gelatin, beeswax, and eggs to stain their nails. The colors were often used to denote social class. Gold and silver was worn by royalty or black and red. The lower classes were not prohibited to wear bright colours.
Lipstick has also a few recipes. Egyptians used pounded carmine, a kind of insect, to smear on their lips. Other ancient civilizations used red ochre. Vermilion (though toxic) was also used, along with crushed flowers with red pigment mixed with beeswax during the Elizabethan period.
During the late Elizabeth and then again in the Baroque period, women and some men began to paint their faces with white powder. The layer of white lead and vinegar, or ceruse was popular for tears despite the hair loss and death it caused.
Make Up Tools

Powderpuffs: the powderpuff was a pad of soft material meant to apply powder to one's face. They were made of feathers, cotton or sheep's fleece.
Brushes: Brushes have been been around for ever. They have been found in some of the earliest Egyptian tombs. The brushes were often made from animal hair with wooden or more expensive handles.
Pots of pigment, scents and ointments: Some early tombs excavated from ancient civilizations have included what amounts to a palette (thank you lil sis for that word). The pigments in the pots would be very expensive. Ointments and balms have also been found. Perfumes were very popular in antiquity and made a recurrence in Europe after the Crusades (which helped since some of the make up smelled awful).
Make Up and Social standing


Though make up is rather popular now, it had a rather uncertain rise to popularity.
Most Ancient civilizations wore some kind of cosmetic. The overuse of cosmetics in ancient times was frowned on as prostitutes and actors often wore dramatic make up however the elite often smeared themselves with powders to make them paler and redden their cheeks.
In the Middle Ages, makeup had a dual reputation. The Church frowned on it because it was again popular with prostitutes and actors but it was a common consensus that if the woman was scarred from smallpox or some other disease she was excused from being labelled as vain.
In the late Elizabethan period, theatres were getting more popular and as was makeup. Actors began wearing make up more frequently as did the elite. Elizabeth I herself was infamous for her milk-white skin. Make up became more sociably acceptable among the rich and noble at this point.
The 1700s probably saw the height of make up madness. Both women and men of the elite powdered themselves with white lead paint. They rouged their cheeks to high pigment and stuck small dots of felt to cover blemishes. The commons began to poke fun at the elite's strange obsession with looking like they've lost all their blood. Dandies and painted noblewomen were often poked fun at by pamphlets and satirical cartoons.
The Victorians frowned on make up, thinking it garish and common. Queen Victoria herself denounced make up as uncouth which lead the elite to abandon it in droves. However, most women prized a clear complexion so there was a lot of secret make-up-ing going on.
During the Edwardian period and the 1920s, make up began to get more popular. Older more respectable women began trying makeup to fresh their complexion. The younger generations began to experiment with makeup leading to the infamous smokey eye look.
My Favourite Couples Are Those Who Could’ve Been Amazing Friends Or Lovers And Work Well As Both But Prefer Friends
This doesn’t make much sense in retrospect but a good example would be Percabeth. Sure, they’re the power couple of the century, but I think they’d work very much better as good friends. Like siblings almost. You know?
I also love giving them meds and drugs. Like, an empath needs anti-depressants, mood-stabilisers, etc. And there are special therapists for empaths, by law in many territories, any person showing signs of being an empath must take a government-issued test and, if empathy positive, are assigned a government approved therapist.
Happy Storyteller Saturday! Do any of your characters wear glasses? I recently got a pair, and the world is much sharper than it used to be!
I’ve been thinking that perhaps they should, as well as rethinking my “supes never get sick” rule. As it stands, there are enchanted glasses that help with eyestrain, translations, and seeing through glamours, but no one I’ve written so far needs them correctively