Random Medical Facts To Use For Your Hospital Whump Writing. Let Your Whumpee Be A Patient Today!
random medical facts to use for your hospital whump writing. let your whumpee be a patient today!
if a patient has a seizure that lasts longer than 5 minutes, or if they suffer several seizures, they risk sustaining brain damage — because their brain can’t get oxygen during the seizure.
if a patient’s coughing up blood when they’re lying on their back, make sure to tune their face to the side so that they don’t choke on their own blood (the same applies to vomit too)
chest compression can and often leave patients with broken ribs. because you have to push down hard enough in order to help pump blood from the patient’s heart to their brain (the point is so that the brain gets blood, in order to prevent brain damage), and more often than not, you’ll end up breaking your patient’s ribs — that is normal and okay, because it’s better for your patient to have broken ribs than it is for them to lose their life.
after a course of electroconvulsive therapy, you’ll normally have to give your patient a dose of muscle relaxant, otherwise the aftermath of the shock may cause musculoskeletal complications.
you don't use a defibrillator to shock a patient if they already flat line, because their heart no longer has any electricity. quote "asystole isn't a shockable rhyme, and defibrillator may actually make it harder to restart the heart." (Cleveland Clinic)
the famous, classic "a character was knocked out and they stayed unconscious for hours before they woke up on their own with no lingering damage" trope is actually almost impossible if you want your work to be medically accurate (but if you don’t care about accuracy and are just here for the whump, that is totally fine!). if someone was knocked out and they stayed unconscious for more than several minutes, chances are that they suffer permanent brain damage, so they won't "wake up on their own in the next hour or two and be completely fine without intense medical attention".
More Posts from Writersreferencez and Others
Showing 'Fear' in Writing
Eyes wide with pupils dilated.
Hands trembling uncontrollably.
Heart pounding audibly in the chest.
Backing away slowly, seeking escape.
Holding breath or breathing shallowly.
Breaking out in a cold sweat.
Startling at the slightest sound.
Whispering or speaking in a hushed tone.
Looking over their shoulder repeatedly.
Clutching at clothing or objects for reassurance.
Voice quivering or stammering.
Legs feeling weak or buckling.
Feeling a chill run down the spine.
Hugging oneself protectively.
Trying to make themselves smaller.
Furtive glances around the room.
Feeling light-headed or dizzy.
Stiffening up and freezing in place.
Swallowing hard, throat dry.
Eyes darting around, unable to focus.
How to Write Betrayal
Betrayal is a powerful plot element that is represented in countless stories. The gravity of betrayal brings a profound depth to character dynamics, plots, and themes alike, making it an indispensable tool for writers to explore emotions, conflicts, and the complexities of human nature. Let’s explore some quick tips on how to write betrayal!
Behaviour
Secretive actions
Dishonesty
Becoming emotionally distant
A sudden change in routine
Pushing people away
Nervous or fidgety movement
Frequent lying or making up stories
Unexpected aggression or irritability
Unjustified mood swings or emotional outbursts
Increasingly defensive
Interactions
Disturbed interpersonal relationships
Frequent misunderstandings or fights
Withholding information
Avoiding personal discussions
Insincerity in conversations
Frequently cancelling or missing plans
A sudden shift in relationship dynamics
Quick to deflect or place blame
Frequent subject changes
Gradual emotional detachment
Body Language
Avoiding direct eye contact
Defensive stance and crossed arms
Covering mouth or touching face
Shuffling or restless movements
Forcing smiles or laughter
Constantly looking around or at the ground
Stiff, tense posture
Heavy breathing or frequent sighing
Avoiding touch or skin contact
Exaggerated gestures
Attitude
A lack of concern or empathy
Increasingly personal and hurtful arguments
Erratic or unpredictable reactions
Self-centeredness
Insincerity
Dismissive or negative attitude
Callous disregard for other's feelings
A negative or pessimistic outlook
Inability to handle criticism
Withdrawal from relationships
Positive Story Outcomes
In the wake of a betrayal, a story can manifest various positive outcomes that add depth to the plot and its characters. Relationships can be strengthened, showing their resilience. Characters may discover newfound self-reliance and learn valuable lessons about trust and forgiveness, leading to an increase in empathy and understanding, personal growth, and the reinforcement of personal values. These experiences can encourage a clearer understanding of personal boundaries, prompt self-reflection, introspection, and the development of healthier coping mechanisms. Ultimately, these positive outcomes can bring about improved communication and honesty, forming the silver lining in the cloud of betrayal.
Negative Story Outcomes
The aftershocks of betrayal can reverberate throughout your story. This might include an irreparable fracture of trust and damage to relationships. Betrayal can trigger psychological trauma, leading to an increase in suspicion and insecurity. Feelings of inadequacy or self-blame may surface, and characters can experience a heightened sense of isolation. The fear of forming new relationships or trusting others can become overwhelming. There may also be an escalation of conflict or violence and the reinforcement of negative behaviours or patterns. Damaged self-esteem or self-worth may be another repercussion, and this can encourage destructive coping mechanisms.
Helpful Synonyms
Treachery
Deception
Double-crossing
Duplicity
Backstabbing
Two-faced
Disloyalty
Unfaithfulness
Infidelity
Falseness
Perfidy
Treason
Fraud
Deceit
Slander
Misrepresentation
Falsification
Chicanery
Double-dealing
There is no reason not to love your writing. You did it. You spent time on it. Of course you should talk about it. No. It’s not boasting, nor are you self obsessed. It’s yours. You spent time on it. Not them. Post about your art. Share with everyone. Because it is amazing.
hey writers! OneLook Thesaurus lets you find that word you can’t think of but can describe! go check it out!



Words instead of sighed and frowned?
Sighed - let out a deep audible breath or made a similar sound (such as weariness or relief)
Exhaled - breathed out
Heaved - uttered with obvious effort or with a deep breath
Huffed - emitted puffs (as of breath); usually with indignation or scorn
Insufflated - blew on, into, or in (something)
Puffed - blew in short gusts; exhaled forcibly
Snorted - forced air violently through the nose with a rough harsh sound (to express scorn, anger, indignation, or surprise)
Snuffled - breathed through an obstructed nose with a sniffing sound
Suspired - drew a long deep breath; sighed
Frowned - contracted the brow in displeasure or concentration
Glared - stared angrily or fiercely
Glouted - (archaic) frowned, scowled
Glowered - looked or stared with sullen annoyance or anger
Grimaced - distorted one's face in an expression usually of pain, disgust, or disapproval
Loured - looked sullen; frowned
Moue - a twisting of the facial features in disgust or disapproval
Pouted - showed displeasure by thrusting out the lips or wearing a sullen expression
Scoffed - expressed scorn, derision, or contempt
Scowled - contracted the brow in an expression of displeasure
Sulked - silently went about in a bad mood
Hope this helps. If it inspires your writing in any way, please tag me, or send me a link. I would love to read your work!
More: Word Lists ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
HOW TO WRITE A CHARACTER WHO IS IN PAIN
first thing you might want to consider: is the pain mental or physical?
if it’s physical, what type of pain is it causing? — sharp pain, white-hot pain, acute pain, dull ache, throbbing pain, chronic pain, neuropathic pain (typically caused by nerve damage), etc
if it’s mental, what is the reason your character is in pain? — grief, heartbreak, betrayal, anger, hopelessness, fear and anxiety, etc
because your character will react differently to different types of pain
PHYSICAL PAIN
sharp and white-hot pain may cause a character to grit their teeth, scream, moan, twist their body. their skin may appear pale, eyes red-rimmed and sunken with layers of sweat covering their forehead. they may have tears in their eyes (and the tears may feel hot), but they don’t necessarily have to always be crying.
acute pain may be similar to sharp and white-hot pain; acute pain is sudden and urgent and often comes without a warning, so your character may experience a hitched breathing where they suddenly stop what they’re doing and clench their hand at the spot where it hurts with widened eyes and open mouth (like they’re gasping for air).
dull ache and throbbing pain can result in your character wanting to lay down and close their eyes. if it’s a headache, they may ask for the lights to be turned off and they may be less responsive, in the sense that they’d rather not engage in any activity or conversation and they’d rather be left alone. they may make a soft whimper from their throat from time to time, depends on their personality (if they don’t mind others seeing their discomfort, they may whimper. but if your character doesn’t like anyone seeing them in a not-so-strong state, chances are they won’t make any sound, they might even pretend like they’re fine by continuing with their normal routine, and they may or may not end up throwing up or fainting).
if your character experience chronic pain, their pain will not go away (unlike any other illnesses or injuries where the pain stops after the person is healed) so they can feel all these types of sharp pain shooting through their body. there can also be soreness and stiffness around some specific spots, and it will affect their life. so your character will be lucky if they have caretakers in their life. but are they stubborn? do they accept help from others or do they like to pretend like they’re fine in front of everybody until their body can’t take it anymore and so they can no longer pretend?
neuropathic pain or nerve pain will have your character feeling these senses of burning, shooting and stabbing sensation, and the pain can come very suddenly and without any warning — think of it as an electric shock that causes through your character’s body all of a sudden. your character may yelp or gasp in shock, how they react may vary depends on the severity of the pain and how long it lasts.
EMOTIONAL PAIN
grief can make your character shut themself off from their friends and the world in general. or they can also lash out at anyone who tries to comfort them. (five states of grief: denial, anger, bargaining, depression and eventual acceptance.)
heartbreak — your character might want to lock themself in a room, anywhere where they are unseen. or they may want to pretend that everything’s fine, that they’re not hurt. until they break down.
betrayal can leave a character with confusion, the feelings of ‘what went wrong?’, so it’s understandable if your character blames themself at first, that maybe it’s their fault because they’ve somehow done something wrong somewhere that caused the other character to betray them. what comes after confusion may be anger. your character can be angry at the person who betrayed them and at themself, after they think they’ve done something wrong that resulted in them being betrayed, they may also be angry at themself next for ‘falling’ for the lies and for ‘being fooled’. so yes, betrayal can leave your character with the hatred that’s directed towards the character who betrayed them and themself. whether or not your character can ‘move on and forgive’ is up to you.
there are several ways a character can react to anger; they can simply lash out, break things, scream and yell, or they can also go complete silent. no shouting, no thrashing the place. they can sit alone in silence and they may cry. anger does make people cry. it mostly won’t be anything like ‘ugly sobbing’ but your character’s eyes can be bloodshot, red-rimmed and there will be tears, only that there won’t be any sobbing in most cases.
hopelessness can be a very valid reason for it, if you want your character to do something reckless or stupid. most people will do anything if they’re desperate enough. so if you want your character to run into a burning building, jump in front of a bullet, or confess their love to their archenemy in front of all their friends, hopelessness is always a valid reason. there’s no ‘out of character’ if they are hopeless and are desperate enough.
fear and anxiety. your character may be trembling, their hands may be shaky. they may lose their appetite. they may be sweaty and/or bouncing their feet. they may have a panic attack if it’s severe enough.
and I think that’s it for now! feel free to add anything I may have forgotten to mention here!

Fear Elements for Your Fiction
Places Creepy places make atmospheric fiction settings.
Is there a place that makes you feel cold? Are you terrified of walking a certain path, especially in the dark?
Recall a scary dream. Where did that dream take place?
Wierd Shudders Are you frightened of something that others people consider harmless?
The sight of long fingernails, the sound of nails scraping on a blackboard. Moths and butterflies flying in your face?
If you have a shudder that makes you feel low-key creeped out in daily life write about it.
Phobias Many people of phobias about particular objects and situations. If you have a phobias, try writing about it.
Childhood Fears Whether the danger was true or imagined, the fear you experienced in your childhood was probably intense.
What if there really was a monster under your bed?
Gian black steam engines, the blue glow of an automatic door lock, the gaping hole of an empty closet?
Dreams Do you have a recurring nightmare? Something that makes you wake up with sweat?
Human Attitudes What are some things that people do that you find scary or creepy?
Unbending bureaucracy? Bullying? People consuming others' pain for entertainment? Hating others in the name of religion?
Use fiction to address these issues.
Ordinary Things Look around the ordinary things around you and ask - what if they aren't as harmless as they seem?
Metal pins on my bulletin board? Windows? The TV? A potted tomato slowly withering?
─── ・ 。゚☆: *.☽ .* . ───
💎If you like my blog, buy me a coffee☕ and find me on instagram!
💎Before you ask, check out my masterpost part 1 and part 2
💎For early access to my content, become a Writing Wizard
Good tips for writing anything, not just role-plays!!
Common grammatical errors and how to correct them!
your vs. you’re
your: belonging to you. For instance “Is this your bag?”
you’re: an abbreviation of you are. For instance “You’re so nice.”
they’re vs. their vs. there
they’re: an abbreviation of they are. For instance “They’re coming this way.”
their: belonging to a group of people or person of unspecified gender. For instance “This is their classroom.”
there: referring to a place. For instance “Will you follow me over there?”
The word “independent” contains no a’s. Commas can change the whole meaning of a phrase. For instance: Let’s eat grandma! vs. Let’s eat, grandma! A good rule of thumb for comma usage (although not perfect) is to read the sentence aloud. If you find yourself pausing between words, that’s a good indication a comma should be there.
Capitalization Proper nouns should be capitalized. This includes names of people, places, and things. However, other nouns will not need it. For instance: you would capitalize “Susan”, ”New York”, and “Eiffel Tower” because those are proper names, but things like “that girl”, “this city”, and “the structure” wouldn’t need it. The first word of a sentence should also be capitalized!
I hope this helps all of you wonderful writers! Have a lovely day and enjoy your RPing! <3
Showing 'Exhaustion' in Writing
Heavy eyelids, struggling to stay open.
Slumping shoulders, barely able to hold themselves up.
Dragging feet with each step.
Speaking in a slow, slurred manner.
Dark circles under the eyes.
Yawning frequently and deeply.
Head nodding forward, trying to stay awake.
Leaning heavily against walls or furniture.
Rubbing eyes and face with hands.
Deep, weary sighs escaping lips.
Wincing at bright lights or loud sounds.
Staring blankly ahead, unable to focus.
Weak, unsteady movements.
Muttering incoherently to themselves.
Falling asleep in unusual places.
Lack of response or delayed reactions.
Propping their head up with their hand.
Collapsing onto the nearest available surface.
Swaying slightly on their feet.
Barely lifting their head to speak or listen.
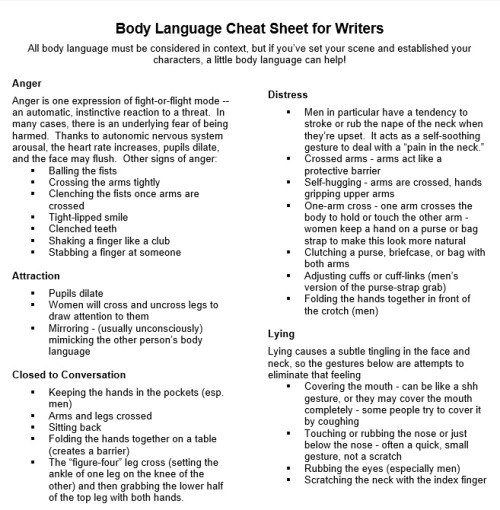

Body Language Cheat Sheet for Writers
As described by Selnick’s article:
Author and doctor of clinical psychology Carolyn Kaufman has released a one-page body language cheat sheet of psychological “tells” (PDF link) fiction writers can use to dress their characters.
-
 sms4chatons liked this · 1 week ago
sms4chatons liked this · 1 week ago -
 444iiionee reblogged this · 1 week ago
444iiionee reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 duckieed liked this · 1 week ago
duckieed liked this · 1 week ago -
 a-certain-type-of-tree liked this · 1 week ago
a-certain-type-of-tree liked this · 1 week ago -
 writtenmostardently liked this · 1 week ago
writtenmostardently liked this · 1 week ago -
 strlghtprncss liked this · 1 week ago
strlghtprncss liked this · 1 week ago -
 jvstjvmp liked this · 1 week ago
jvstjvmp liked this · 1 week ago -
 milfs4ten liked this · 1 week ago
milfs4ten liked this · 1 week ago -
 indigo-skies2315 reblogged this · 1 week ago
indigo-skies2315 reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 fufikitty liked this · 1 week ago
fufikitty liked this · 1 week ago -
 dreamscxpee liked this · 1 week ago
dreamscxpee liked this · 1 week ago -
 steven-the-frog liked this · 1 week ago
steven-the-frog liked this · 1 week ago -
 periwinkle-of-ireland liked this · 1 week ago
periwinkle-of-ireland liked this · 1 week ago -
 spinelessfilament liked this · 1 week ago
spinelessfilament liked this · 1 week ago -
 odysseusandorpheus liked this · 1 week ago
odysseusandorpheus liked this · 1 week ago -
 snails-n-frogs liked this · 1 week ago
snails-n-frogs liked this · 1 week ago -
 fitz4fool liked this · 1 week ago
fitz4fool liked this · 1 week ago -
 kiokijin reblogged this · 1 week ago
kiokijin reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 kiokijin liked this · 1 week ago
kiokijin liked this · 1 week ago -
 alwayspleasanttragedy liked this · 1 week ago
alwayspleasanttragedy liked this · 1 week ago -
 sirbonesly reblogged this · 1 week ago
sirbonesly reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 sirbonesly liked this · 1 week ago
sirbonesly liked this · 1 week ago -
 quiteimpossibletodescribe liked this · 2 weeks ago
quiteimpossibletodescribe liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 skele-was-hired liked this · 2 weeks ago
skele-was-hired liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 blueberriekid liked this · 2 weeks ago
blueberriekid liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 lolrpop liked this · 2 weeks ago
lolrpop liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 staleclown liked this · 2 weeks ago
staleclown liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 mypersonalhologram liked this · 2 weeks ago
mypersonalhologram liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 karra-night liked this · 2 weeks ago
karra-night liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 nobodycanhavethisusername1 liked this · 2 weeks ago
nobodycanhavethisusername1 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 badbyeuhgood liked this · 2 weeks ago
badbyeuhgood liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 captain-daryn liked this · 2 weeks ago
captain-daryn liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 n0-1-important reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
n0-1-important reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 n0-1-important liked this · 2 weeks ago
n0-1-important liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 crestfallercanyon liked this · 2 weeks ago
crestfallercanyon liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 thaliaisalesbian reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
thaliaisalesbian reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 holiday-spice liked this · 2 weeks ago
holiday-spice liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 ejtyler liked this · 2 weeks ago
ejtyler liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 valengory1234 liked this · 2 weeks ago
valengory1234 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 shiny-good-rock liked this · 2 weeks ago
shiny-good-rock liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 pennythemechpilot liked this · 2 weeks ago
pennythemechpilot liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 hiddensquid13 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
hiddensquid13 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 hiddensquid13 liked this · 2 weeks ago
hiddensquid13 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 rachelthesilly liked this · 2 weeks ago
rachelthesilly liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 sweetiepie08 liked this · 2 weeks ago
sweetiepie08 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 givemeallyourpenny reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
givemeallyourpenny reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 givemeallyourpenny liked this · 2 weeks ago
givemeallyourpenny liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 jedidragonwarriorqueen reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
jedidragonwarriorqueen reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 jedidragonwarriorqueen liked this · 2 weeks ago
jedidragonwarriorqueen liked this · 2 weeks ago