T-b-a-blr-blog - Untitled

More Posts from T-b-a-blr-blog and Others
Gram Negative Aerobic Rods Mnemonic
MICROBIOLOGY MNEMONIC
BRUno, FRANCISco & COnstantine are BORing PSEUDO LEGIONnaires
Brucella sp
Francisella tularensis
Coxiella burnetti
Bortedella pertusis
Pseudomona aeuroginosa
Legionella pneumophila







Immuno
Microbiology Mnemonic
STD: Chlamydia Trachomatis’ serotypes
“Eye Don't Know why people don’t use condoms”
Most common BACTERIAL STD in the US
Serotypes: D-K : nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, PID
Eye: Inclusion conjunctivitis.
Pneumonia (staccato cough) / Inclussion conjunctivitis in neonates / infants

STD: L imphogranuloma Venereum
L1,2,3
Africa, Asia, South America
Swollen lymph nodes, ulcers, fistulas -> Genital elephantiasis

tr AC homa
A-C serotypes (A,B,Ba,C)
Follicular conjuntivitis -> Conjuntival scarring -> inturned eyelashes -> corneal scarring -> BLINDNESS


Actinomyces israelii
Gram+, anaerobic, non-spore forming, branching rod
Endogenous transmission (dental crevices -bad higiene, dental trauma- ; female genital tract -IUD-)
Dx: branching rods in “sulfur granules”; colonies resemble a molar tooth.


Not painful but very invasive penetrating tissues, including bone.
Draining abscess (sinus tracts) CULTURE THAT PUS
Disease: ACTINOMYCOSIS in low O2 tissues
Cervicofacil: “Lumpy jaw”, mycetoma on jaw line
Pelvic: from IUD
CNS: solitary abscess
Abdominal: qx, trauma
Thoracic: aspiration

Haematology
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)

Neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils = granulocytes (polymorphonuclear leukocytes)
Monocytes & lymphocyes = mononuclear
Neutrophils
Most numerous (~60% of WBC)
Nucleus divided into lobes
Cytoplasm contains small granules
Stains pink with Romanowsky dyes
Lifespan of 6-10hrs
Exit into tissues - non-specific defence against bacteria and fungi

Eosinophils
1% of circulating leukocytes
Large cytoplasmic granules - stain strongly with acidic dye eosin
Nucleus is bilobed
Circulate for 4-5hrs
Exit to tissues –>
Defence against parasites
Dampen allergic response
Tissue eosinophils are also capable of responding to bacterial and fungal infection in a similar way to neutrophils.

Basophils
Least numerous (<1%)
Large granules stain strongly with basic dye methylene blue
Involved in anaphylactic hypersensitivity and inflammatory reactions

Monocytes
5% of circulating leukocytes
Large cell
Kidney/clefted shaped nucleus
Scattering of delicate azurophilic granules
Circulate for 10hrs
Mature into phagocytic tissue macrophages
Responsible for the removal of aged RBCs and other debris
Process and present antigens to T-lymphocytes

(Macrophages are formed in response to an infection or accumulating damaged or dead cells. Large, specialized cells that recognize, engulf and destroy target cells.)

Lymphocytes
Second most common leukocyte (33%)
Much less cytoplasm - nucleus almost fills cell
Variable lifespan
Receptors on surface recognise foreign substances

Several types of lymphocyte - click here
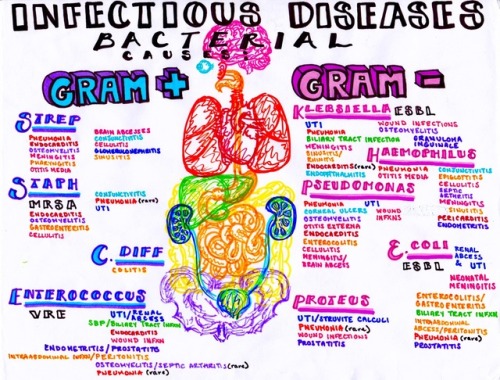
Infectious bacterial diseases and where to find them

Elementary body of Chlamydia trachomatis in a conjunctival scrapping in a patient with trachoma: Trachoma is the MCC of preventive global blindness


Prokaryotic cell
-
 annadbsp6 liked this · 6 months ago
annadbsp6 liked this · 6 months ago -
 ward121 liked this · 1 year ago
ward121 liked this · 1 year ago -
 domaldtrump liked this · 1 year ago
domaldtrump liked this · 1 year ago -
 gaconsnecjusu liked this · 1 year ago
gaconsnecjusu liked this · 1 year ago -
 hey-pretinha-blog liked this · 1 year ago
hey-pretinha-blog liked this · 1 year ago -
 efendiorangutan liked this · 2 years ago
efendiorangutan liked this · 2 years ago -
 melissa-loveseex221981-blog liked this · 3 years ago
melissa-loveseex221981-blog liked this · 3 years ago -
 ywnyfm liked this · 3 years ago
ywnyfm liked this · 3 years ago -
 samimie31 liked this · 3 years ago
samimie31 liked this · 3 years ago
