Affect Is Something That Physically Affects Something
Affect is something that physically affects something
Effect is a direct result of a certain cause.
Honestly, knowing that it's still hard to determine which one to use

More Posts from Writersreferencez and Others
Actually
The question I get the most is how I write characters that feel like real people.
Generally when I’m designing a human being, I deconstruct them into 7 major categories:
1. Primary Drive 2. Fear: Major and Secondary 3. Physical Desires 4. Style of self expression 5. How they express affection 6. What controls them (what they are weak for) 7. What part of them will change.
1. Primary Drive: This is generally related to the plot. What are their plot related goals? How are they pulling the plot forward? how do they make decisions? What do they think they’re doing and how do they justify doing it. 2. Fear: First, what is their deep fear? Abandonment? being consumed by power? etc. Second: tiny fears. Spiders. someone licking their neck. Small things that bother them. At least 4. 3. Physical desires. How they feel about touch. What is their perceived sexual/romantic orientation. Do their physical desires match up with their psychological desires.
4. Style of self expression: How they talk. Are they shy? Do they like to joke around and if so, how? Are they anxious or confident internally and how do they express that externally. What do words mean to them? More or less than actions? Does their socioeconomic background affect the way they present themselves socially? 5. How they express affection: Do they express affection through actions or words. Is expressing affection easy for them or not. How quickly do they open up to someone they like. Does their affection match up with their physical desires. how does the way they show their friends that they love them differ from how they show a potential love interest that they love them. is affection something they struggle with?
6. What controls them (what they are weak for): what are they almost entirely helpless against. What is something that influences them regardless of their own moral code. What– if driven to the end of the wire— would they reject sacrificing. What/who would they cut off their own finger for. What would they kill for, if pushed. What makes them want to curl up and never go outside again from pain. What makes them sink to their knees from weakness or relief. What would make them weep tears of joy regardless where they were and who they were in front of.
7. WHAT PART OF THEM WILL CHANGE: people develop over time. At least two of the above six categories will be altered by the storyline–either to an extreme or whittled down to nothing. When a person experiences trauma, their primary fear may change, or how they express affection may change, etc. By the time your book is over, they should have developed. And its important to decide which parts of them will be the ones that slowly get altered so you can work on monitoring it as you write. making it congruent with the plot instead of just a reaction to the plot.
That’s it.
But most of all, you have to treat this like you’re developing a human being. Not a “character” a living breathing person. When you talk, you use their voice. If you want them to say something and it doesn’t seem like (based on the seven characteristics above) that they would say it, what would they say instead?
If they must do something that’s forced by the plot, that they wouldn’t do based on their seven options, they can still do the thing, but how would they feel internally about doing it?
How do their seven characteristics meet/ meld with someone else’s seven and how will they change each other?
Once you can come up with all the answers to all of these questions, you begin to know your character like you’d know one of your friends. When you can place them in any AU and know how they would react.
They start to breathe.
In Which Diversity Isn't a Myth
Ok. I’m tired of the typical vampire, werewolf and fairy.I’m also tired of the occidental-centrism in mythology. Hence, this list.
I tried to included as many cultural variants as I could find and think of. (Unfortunately, I was restricted by language. Some Russian creatures looked very interesting but I don’t speak Russian…) Please, add creatures from your culture when reblogguing (if not already present). It took me a while to gather all those sites but I know it could be more expansive. I intend on periodically editing this list.
Of note: I did not include specific legendary creatures (Merlin, Pegasus, ect), gods/goddesses/deities and heroes.
Dragons
The Chinese Dragon
The Japanese Dragon
The Korean Dragon
The Vietnamese Dragon
The Greek Dragon
The Indian Dragon
The Polish Dragon
The Austrian Dragon
The British Dragon
The Ancient Dragon (Egypt, Babylon and Sumer)
The Spanish Basque Dragon
Of the Cockatrice (creature with the body of a dragon)
Alphabetical List of Dragons Across Myths (Great way to start)
Little creatures (without wings)
The Legend of the Leprechauns, The Leprechaun
Chanaque /Alux (the equivalent of leprechauns in Aztec/Mayan folklore)
Elves
Elves in Mythology and Fantasy
Elves in Germanic Mythology
Kabeiroi or Cabeiri (Dwarf-like minor gods in Greek mythology)
Norse Dwarves
The Myth of Loki and the Dwarves
Ten Types of Goblins
Goblins
Tengu: Japanese Goblins
Gnomes
More on Gnomes
Pooka: an Irish phantom
Creatures with wings (except dragons)
Fairies
All sorts of Cultural Fairies
Fairies in Old French Mythology
A Fairy List
Bendith Y Mamau (Welsh fairies)
Welsh Fairies
Peri (Persian fairies)
Yü Nü (Chinese fairies)
The Celtic Pixie
Angels in Judaism
Angels in Christianity
Hierarchy of Angels
Angels in Islam
Irish Sylph
Garuda (Bird-like creature in Hindu and Buddhist myths)
Bean Nighe (a Scottish fairy; the equivalent of a banshee in Celtic mythology)
Harpies
Spirited Creatures
Druids
Jinn (Genies in Arabic folklore)
Types of Djinns
Aisha Qandisha and Djinn in Moroccan Folklore
Oni (demons in Japanese folklore)
Nymphs
Spirits in Asturian Mythology
Valkyries
Lesovik
Boggarts: The British Poltergeist
Phantom black dogs (the Grim)
Demons in Babylonian and Assyrian Mythology (list)
Demons in the Americas (list)
European Demons (list)
Middle-East and Asia Demons (list)
Judeo-Christian Demons (list)
Nephilim, more on Nephilim
Mahaha (a demon in Inuit mythology)
Flying Head (a demon in Iroquois mythology)
Ghosts
Toyol (a dead baby ghost in Malay folklore)
Malay Ghosts
Yuki-onna (a ghost in Japanese folklore)
The Pontianak (a ghost in Malay mythology)
Funayurei (a ghost in Japanese folklore)
Zagaz (ghosts in Moroccan folklore)
Japanese Ghosts
Mexican Ghosts
Horse-like mythical creatures
Chinese Unicorns
Unicorns
The Kelpie (Could have also fitted in the sea creatures category)
The Centaur
The Female Centaur
Hippocamps (sea horses in Greek mythology)
Horse-like creatures (a list)
Karkadann, more on the Karkadann (a persian unicorn)
Ceffyl Dwfr (fairy-like water horse creatures in Cymric mythology)
Undead creatures
The Melanesian Vampire
The Ewe Myth : Vampires
The Germanic Alp
The Indonesian Vampire
Asanbosam and Sasabonsam (Vampires from West Africa)
The Aswang: The Filipino Vampire
Folklore Vampires Versus Literary Vampires
Callicantzaros: The Greek Vampire
Vampires in Malaysia
Loogaroo/Socouyant: The Haitian Vampire
Incubi and Sucubi Across Cultures
Varacolaci: The Romanian Vampire
Brahmaparusha: The Indian Vampire
Genesis of the Word “Vampire”
The Ghoul in Middle East Mythology
Slavic Vampires
Vampires A-Z
The Medical Truth Behind the Vampire Myths
Zombies in Haitian Culture
Shape-shifters and half-human creatures (except mermaids)
Satyrs (half-man, half-goat)
Sirens in Greek Mythology (half-woman and half-bird creatures)
The Original Werewolf in Greek Mythology
Werewolves Across Cultures
Werewolf Syndrome: A Medical Explanation to the Myth
Nagas Across Cultures
The Kumiho (half fox and half woman creatures)
The Sphinx
Criosphinx
Scorpion Men (warriors from Babylonian mythology)
Pooka: an Irish changelings
Domovoi (a shape-shifter in Russian folklore)
Aatxe (Basque mythology; red bull that can shift in a human)
Yech (Native American folklore)
Ijiraat (shapeshifters in Inuit mythology)
Sea creatures
Selkies (Norse mermaids)
Mermaids in many cultures
More about mermaids
Mermen
The Kraken (a sea monster)
Nuckelavee (a Scottish elf who mainly lives in the sea)
Lamiak (sea nymphs in Basque mythology)
Bunyip (sea monster in Aboriginal mythology)
Apkallu/abgal (Sumerian mermen)
An assemblage of myths and legends on water and water creatures
Slavic Water Creatures
The Encantado (water spirits in Ancient Amazon River mythology)
Zin (water spirit in Nigerian folklore)
Qallupilluk (sea creatures in Inuit mythology)
Monsters That Don’t Fit in Any Other Category
Aigamuxa, more details on Aigamuxa
Amphisabaena
Abere
Bonnacon
Myrmidons (ant warriors)
Troll, More on Trolls
Golems
Golems in Judaism
Giants: The Mystery and the Myth (50 min long documentary)
Inupasugjuk (giants in Inuit mythology)
Fomorians (an Irish divine race of giants)
The Minotaur
The Manticore, The Manticore and The Leucrouta
The Ogre
The Orthus (two-headed serpent-tailed dog)
The Windigo
The Windigo Psychosis
Rakshasa (humanoids in Hindu and Buddhist mythology)
Yakshas (warriors in Hindu mythology)
Taqriaqsuit (“Shadow people” in Inuit mythology)
References on Folklore and Mythology Across the Globe
Creatures of Irish Folklore
Folklore and Fairytales
An Overview of Persian Folklore
Filipino Folklore
Myths, Creatures and Folklore
Alaska Folklore
Spanish (Spain) Mythology
Mythical Archive
Mythology Dictionary
List of Medieval and Ancient Monsters
Native American Animals of Myth and Legends
Native American Myths
Bestiary of Ancient Greek Mythology
Mythology, Legend, Folklore and Ghosts
Angels and Demons
List of Sea Creatures
Yoruba Mythology
Ghosts Around the World, Ghosts From A to Z
Strange (Fantastic) Animals of Ancient Egypt
Egyptian Mythology
Creatures from West Africa
On the Legendary Creatures of Africa
Myths, Creatures and Folklore
References on writing a myth or mythical creatures
Writing a MYTHology in your novel?
How to Write a Myth
10 Steps to Creating Realistic Fantasy Creatures
Creating Fantasy Creatures or Alien Species
Legendary Creature Generator
Book Recommendations With Underrated Mythical Creatures
(I have stumbled upon web sites that believed some of these mythical creatures exist today… Especially dragons, in fact. I just had to share the love and scepticism.)
One of the best tips for writing descriptions of pain is actually a snippet I remember from a story where a character is given a host of colored pencils and asked to draw an egg.
The character says that there’s no white pencil. But you don’t need a white pencil to draw a white egg. We already know the egg is white. What we need to draw is the luminance of the yellow lamp and the reflection of the blue cloth and the shadows and the shading.
We know a broken bone hurts. We know a knife wound hurts. We know grief hurts. Show us what else it does.
You don’t need to describe the character in pain. You need to describe how the pain affects the character - how they’re unable to move, how they’re sweating, how they’re cold, how their muscles ache and their fingers tremble and their eyes prickle.
Draw around the egg. Write around the pain. And we will all be able to see the finished product.
Color Synonyms
White

also: pale; blanched; sallow; pallid; waxen; spectral; translucent; albino;
Grey
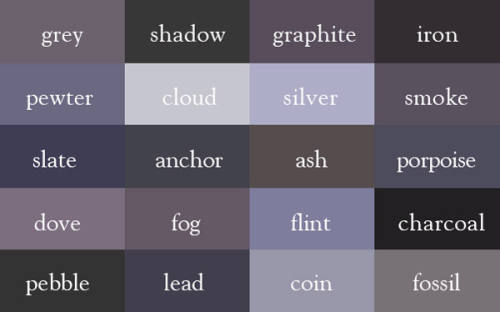
also: dust; stone; pepper;
Black

also: coal; slate; dusky; ebon; shadow; murky;
Tan

also: flesh; khaki; cream; tawny;
Brown

also: henna; russet; sepia; chestnut; cocoa; drab; bronze;
Red

also: terracotta ; rouge; carmine; fire-engine; ruddy
Orange

also: pumpkin ; rust ;
Yellow

also: sunny; amber; saffron; hay; straw; platinum;
Green

also: viridescent; grass; jade; forest;
Blue

also: turquoise; cyan; ultramarine; royal; aqua; aquamarine;
Purple

also: berry; amaranthine;
Pink

also: flushed; candy; cherry blossom; petal pink ;
—– source: http://ingridsundberg.com/
—–additional synonyms added by me
Some words to use when writing things:
winking
clenching
pulsing
fluttering
contracting
twitching
sucking
quivering
pulsating
throbbing
beating
thumping
thudding
pounding
humming
palpitate
vibrate
grinding
crushing
hammering
lashing
knocking
driving
thrusting
pushing
force
injecting
filling
dilate
stretching
lingering
expanding
bouncing
reaming
elongate
enlarge
unfolding
yielding
sternly
firmly
tightly
harshly
thoroughly
consistently
precision
accuracy
carefully
demanding
strictly
restriction
meticulously
scrupulously
rigorously
rim
edge
lip
circle
band
encircling
enclosing
surrounding
piercing
curl
lock
twist
coil
spiral
whorl
dip
wet
soak
madly
wildly
noisily
rowdily
rambunctiously
decadent
degenerate
immoral
indulgent
accept
take
invite
nook
indentation
niche
depression
indent
depress
delay
tossing
writhing
flailing
squirming
rolling
wriggling
wiggling
thrashing
struggling
grappling
striving
straining
Instead of "Looked", consider
glanced
peered
gazed
stared
watched
observed
examined
scrutinized
surveyed
glimpsed
eyed
beheld
inspected
checked
viewed
glanced at
regarded
noticed
gawked
spied
There’s a fic on fanfiction(.)net that I’ve kept tabs on for years to see if it’s been updated or not. While I’m no longer even in the fandom it’s written for, it just has one of the greatest storylines I’ve ever read. Last time it was updated was 2011.
The other day, I decided to reread the entire thing and leave a very in-depth review of what I thought of each chapter. I also mentioned how I started reading it when I was 13 and am now 21, but always came back to see if it was ever finished because I loved it so dearly.
Today, said author sent me a private message saying that her analytics showed that the story was still getting views even after all these years, but no one ever bothered to leave reviews other than “update soon!!!”, so she never felt motivated enough to finish it. She said that me reviewing every single chapter with lengthy paragraphs made her cry and meant the world to her. She also mentioned that she felt encouraged to write the two remaining chapters needed to complete the story and that she would send me a message the night before she updates the fic.
I’m literally sobbing. I’m so excited :’)
Please always remember to leave a review when reading fanfiction!!! It means a lot to a writer.

More bits of writing discussion
The Editing Agenda: Those Darn Dashes

When it comes to formatting and punctuation issues, hyphens and dashes take the cake. Their use in books is incredibly inconsistent, which leads to a lot of confusion for anyone trying to learn them. This article will give a thorough breakdown of each kind and their uses as they pertain to fiction. Keep in mind that the rules I’m covering are the ones that are the most beneficial for fiction writing—there are some that won’t be addressed in this post. And all rules mentioned are based on The Chicago Manual of Style, 16th Edition.
Hyphens
Phrasal Adjectives
Phrasal adjectives are a short group of words (usually two but sometimes three or more) that link together to modify another noun. They typically precede the noun and are very common in fiction writing.
Example 1: rose-colored glasses
Example 2: four-chambered heart
A fantastic resource for this can be found on The Chicago Manual of Style website: http://www.chicagomanualofstyle.org/16/images/ch07_tab01.pdf
This chart shows you the breakdown of various combinations of adjectives and how they should be punctuated, including permanently hyphenated words and exceptions. The CMOS advises following Merriam-Webster’s dictionary for determining which words and phrases should always be hyphenated. Some of examples of this are the words life-form, run-down (not to be confused with rundown, which holds a different meaning), and short-lived.
Compound Name
Hyphens are also used for compound names, including surnames, first names, and other names.
Example 1: Merriam-Webster
Example 2: Mary-Kay
Example 3: Theta-Gamma
Word Division
The most common word division breaks where you’d find hyphens would be line breaks, syllable breaks (often used for pronunciation purposes), and prefixes and suffixes. Which isn’t all that common in fiction writing. However, you will often see it in dialogue, particularly with stuttering.
Example: “W-w-where’d you l-l-leave it?” Tom asked.
Separators
Hyphens can also be used to separate letters and numbers. That’s that type of thing you see with phone numbers, ID numbers, and the like. However, a great use for separation hyphens in fiction writing if when have a word that you need to spell out completely or partially.
Example: The sign read: “C-A-U-T.” The rest had long worn off.
En Dashes
Dates, Times, and Page Numbers
The en dash’s main purpose is to replace the word to. The most typical occurrence of this would be with dates, times, and page numbers.
Example 1: He held office from 1929–1932.
Example 2: The event is Saturday, 2:30p.m.–4:30p.m.
Example 3: Tonight’s assignment is to read pages 32–45.
You also might see this with scoring/votes and with an unfinished number range.
Example 4: We won our last game 13–2.
Example 5: The magazine (2003–) has produced six volumes so far.
However, you should always use the word “to” instead of an en dash if “from” precedes the range.
Example 6: He joined us from 11a.m. to 12p.m. but had to leave for lunch after that.
Directions and Compound Adjectives
En dashes are also sometimes used with words, as can be the case with directions.
Example 1: I took the London–Paris train last week.
And sometimes—very rarely—an en dash is used with compound adjectives. This is where it gets tricky because the intended meaning can often get muddled by using this method, so it’s usually best to reword and find a more elegant solution when possible.
Example 2a: I’d like to find more Taylor Swift–style music.
Example 2b: I’d like to find more artists like Taylor Swift.
Version 2b of the above example flows much better and is less confusing than the first, so it’s definitely the better choice.
And with two sets of compound adjectives where the sets are acting as coordinate adjectives to each other, a comma is the best option.
Example 3: This run-down, high-maintenance property will end up costing a lot of money.
Universities
The last use of en dashes is one that you probably won’t find in most fiction writing, but it’s useful to know nonetheless. You will sometimes find universities with multiple campus locations using an en dash to include the location name.
Example: I put my application in for Fordham University–Westchester.
Em Dashes
Em dashes are used to set off phrases and clauses in a manuscript that require an abrupt break, either to draw attention to it or because there is a large shift in the train of thought. This is one of the most useful tools an author has in fiction writing when it’s used correctly and sparingly. Note that em dashes should NOT be substituted with ellipses; the two serve different purposes.
Em Dashes vs. Ellipses
Em dashes are used for interruption or to set off an explanatory element. An ellipsis is used to indicate hesitation or trailing off.
Example 1: “Lucy, where did you put—”
“It’s none of your business!” Lucy shouted from the other room.
Example 2: I stumbled down the stairs—the power had gone out earlier that evening—before I found my way to the bathroom.
Example 3: “I don’t know…” I admitted. “I hadn’t really thought much about it.”
Interrupted Thoughts
Sometimes the interruptions can come in the form of narrative thoughts.
Example: Justin’s feet pounded against the ground as he blazed down the trail. Awesome. If he kept up the pace, he’d beat—a tree root caught his foot, and he was sent sprawling into the dirt.
And if you have a character that is having trouble forming a sentence due to the circumstances at hand and/or heighted emotions, em dashes can be used to indicate stammering between words (not syllables).
Example: “What I meant was—why can’t we—oh, just forget it,” Julie spat out.
Words and Phrases
An em dash can also be used to set off noun or pronoun at the beginning of the sentence.
Example: Cowards—they were the ones who sought power.
Another common use for the em dash is before the phrases “namely,” “that is,” “for example,” and others similar to those.
Example: We spent most of the afternoon in the garden—that is, until the heat got to be unbearable.
Note: You should never use em dashes within or immediately following an element that already has a set of em dashes. Not only would this look terrible aesthetically, but it could also cause potential misinterpretation.
Interrupted Dialogue
The last use of em dashes for fiction is probably one of the trickiest, but it can also be the most useful. If you have a line of dialogue that is split up by an action in the middle, you can use em dashes to set off that action.
Example 1: “Well, the thing is”—Tommy quickly turned his attention to his feet—“it’s just not working out between us.”
Note that the em dashes go outside of the quotation marks in such a case, and the quotation is a continuous line of dialogue that is being split. The first word of the dialogue after the split should be lowercase. You can’t use this method if you have two separate sentences that have an action in between. In that situation, you’d use periods.
Example 2: “You really mean it.” I could hear my voice catch in my throat. “I just don’t understand what happened.
Two-Em Dash
One type of em dashes that is not commonly used in fiction writing that is probably my favorite is the 2-em dash. The 2-em dash is used to omit words or parts of words that are missing or illegible, or to conceal a name. Two em dashes are most useful for the genres of fantasy, thriller, and mystery, where characters might come across documents that have damage to them. The example below is from a snippet of a work in progress of mine: book one of the Ansakerr series.
My dearest I——,
If you are reading this, I have long since p—— away. I can only pray that my —— box and this letter have fallen into your hands and your hands alone. There is much you have yet learn to about me. There is still a D——k O—— out there, one more dangerous than you can imagine. For now, you are protected, but be on your toes, my girl. One day soon, I fear the p—— will fade, and you’ll need to be ready. He is coming.
The key will lead you to A——. It will hold the answers you’re looking for.
Deepest love and affection,
Grandma Bea
Notice that most of the missing parts are for key elements, including names, places, and very specific items that are clearly key for the plot. If you craft these parts well, you can purposely mislead a reader in the narrative, giving a bit of a twist to your story.
Formatting and Stylistic Use
No spaces should be used around hyphens or dashes except in the case of the 2-em dash when it is being used to completely omit a word. This is probably the most common error regarding formatting of hyphens and dashes that I come across. Though there is some debate about spacing among various sources, the CMOS is pretty clear about it. But again, as with anything else in writing, consistency is the most important.
As for formatting the different dashes, mainstream word processors include symbols for each that you can insert into your document. In fact, some of them even automatically convert two hyphens used together into an em dash. While most publishers will accept em dashes in the form of two hyphens (in fact, some even request that you submit manuscripts that way), when it comes to actual printing and online publishing of the material, you’ll want to make sure they’re replaced. Your document will look more professional when you use the correct symbol, and your readers will likely notice as well.
Tip: To quickly find and replace any stray instances of two hyphens with an em dash symbol, use your word processors Replace function.
Lastly, when it comes to use with other punctuation, a question mark or an exclamation mark can precede an em dash, but never a comma, colon, or semicolon. In other words, if you use an em dash where one of the latter punctuation marks would typically be used, the dash takes the place of the punctuation.
Example: He bent down to tie his shoe—but he stopped when he saw Alyssa approaching.

Seven years after, I see you again 😚
-
 promiscuousasexual reblogged this · 1 year ago
promiscuousasexual reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 hhhhhhhhyuhghhv reblogged this · 1 year ago
hhhhhhhhyuhghhv reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 hhhhhhhhyuhghhv liked this · 1 year ago
hhhhhhhhyuhghhv liked this · 1 year ago -
 shanxy180 liked this · 3 years ago
shanxy180 liked this · 3 years ago -
 shanxy180 reblogged this · 3 years ago
shanxy180 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 queer-and-nd-coded liked this · 3 years ago
queer-and-nd-coded liked this · 3 years ago -
 zygomatikprocess liked this · 3 years ago
zygomatikprocess liked this · 3 years ago -
 bobolovesoze liked this · 3 years ago
bobolovesoze liked this · 3 years ago -
 bisexual-dumbass-blog reblogged this · 3 years ago
bisexual-dumbass-blog reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 bisexual-dumbass-blog liked this · 3 years ago
bisexual-dumbass-blog liked this · 3 years ago -
 mothmans-favorite-lamp liked this · 3 years ago
mothmans-favorite-lamp liked this · 3 years ago -
 onewiththedemons liked this · 3 years ago
onewiththedemons liked this · 3 years ago -
 chekovs-fuckup reblogged this · 3 years ago
chekovs-fuckup reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 chekovs-fuckup liked this · 3 years ago
chekovs-fuckup liked this · 3 years ago -
 thnks4thstrdst liked this · 3 years ago
thnks4thstrdst liked this · 3 years ago -
 spacellama23 reblogged this · 3 years ago
spacellama23 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 spacellama23 liked this · 3 years ago
spacellama23 liked this · 3 years ago -
 the-fuckery-factory reblogged this · 3 years ago
the-fuckery-factory reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 the-fuckery-factory liked this · 3 years ago
the-fuckery-factory liked this · 3 years ago -
 ashleytannous-blog liked this · 3 years ago
ashleytannous-blog liked this · 3 years ago -
 sweetsorrow-love liked this · 3 years ago
sweetsorrow-love liked this · 3 years ago -
 reddragdiva liked this · 3 years ago
reddragdiva liked this · 3 years ago -
 hennethgalad reblogged this · 3 years ago
hennethgalad reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 hennethgalad liked this · 3 years ago
hennethgalad liked this · 3 years ago -
 marnanel reblogged this · 3 years ago
marnanel reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 era-growing liked this · 4 years ago
era-growing liked this · 4 years ago -
 leisavery liked this · 4 years ago
leisavery liked this · 4 years ago -
 argeraakigeminuga-palun liked this · 4 years ago
argeraakigeminuga-palun liked this · 4 years ago -
 ho3foryou liked this · 4 years ago
ho3foryou liked this · 4 years ago -
 loonyloveg00d reblogged this · 4 years ago
loonyloveg00d reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 thaiika liked this · 4 years ago
thaiika liked this · 4 years ago -
 lilywill21 liked this · 4 years ago
lilywill21 liked this · 4 years ago -
 swinginwobblerlawyerflap liked this · 4 years ago
swinginwobblerlawyerflap liked this · 4 years ago -
 o-isnt-she-lovely liked this · 4 years ago
o-isnt-she-lovely liked this · 4 years ago -
 mystuffsstuff liked this · 4 years ago
mystuffsstuff liked this · 4 years ago -
 sweet-bumble-bee reblogged this · 5 years ago
sweet-bumble-bee reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sagitariusartist liked this · 5 years ago
sagitariusartist liked this · 5 years ago -
 denaayling93 liked this · 5 years ago
denaayling93 liked this · 5 years ago -
 doctorclione liked this · 5 years ago
doctorclione liked this · 5 years ago -
 skulmam liked this · 5 years ago
skulmam liked this · 5 years ago -
 ninjakittenarmy reblogged this · 5 years ago
ninjakittenarmy reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 theculturedmarxist reblogged this · 5 years ago
theculturedmarxist reblogged this · 5 years ago